How Long Does the Flu Last? A Detailed Guide to Understanding Flu Duration
Influenza, commonly known as the flu, is a contagious respiratory illness that affects millions of people worldwide each year. Understanding how long the flu lasts is crucial for managing symptoms, preventing the spread of the virus, and knowing when to seek medical attention.
Key Takeaways
- The flu typically lasts about 5 to 7 days, but symptoms can linger longer in some cases.
- Rest, hydration, and over-the-counter medications can help alleviate symptoms.
- Flu vaccines are the most effective way to prevent the flu.
- Seek medical attention if severe symptoms or complications arise.
Understanding the Flu: An Overview
The flu is caused by the influenza virus, which infects the nose, throat, and sometimes the lungs. It can lead to mild to severe illness and, in some cases, can be fatal. The virus spreads through droplets when an infected person coughs, sneezes, or talks, making it highly contagious.
Symptoms of the Flu

Flu symptoms often come on suddenly and can include:
- Fever or feeling feverish/chills
- Cough
- Sore throat
- Runny or stuffy nose
- Muscle or body aches
- Headaches
- Fatigue (tiredness)
- Some people may experience vomiting and diarrhea, though this is more common in children than adults.
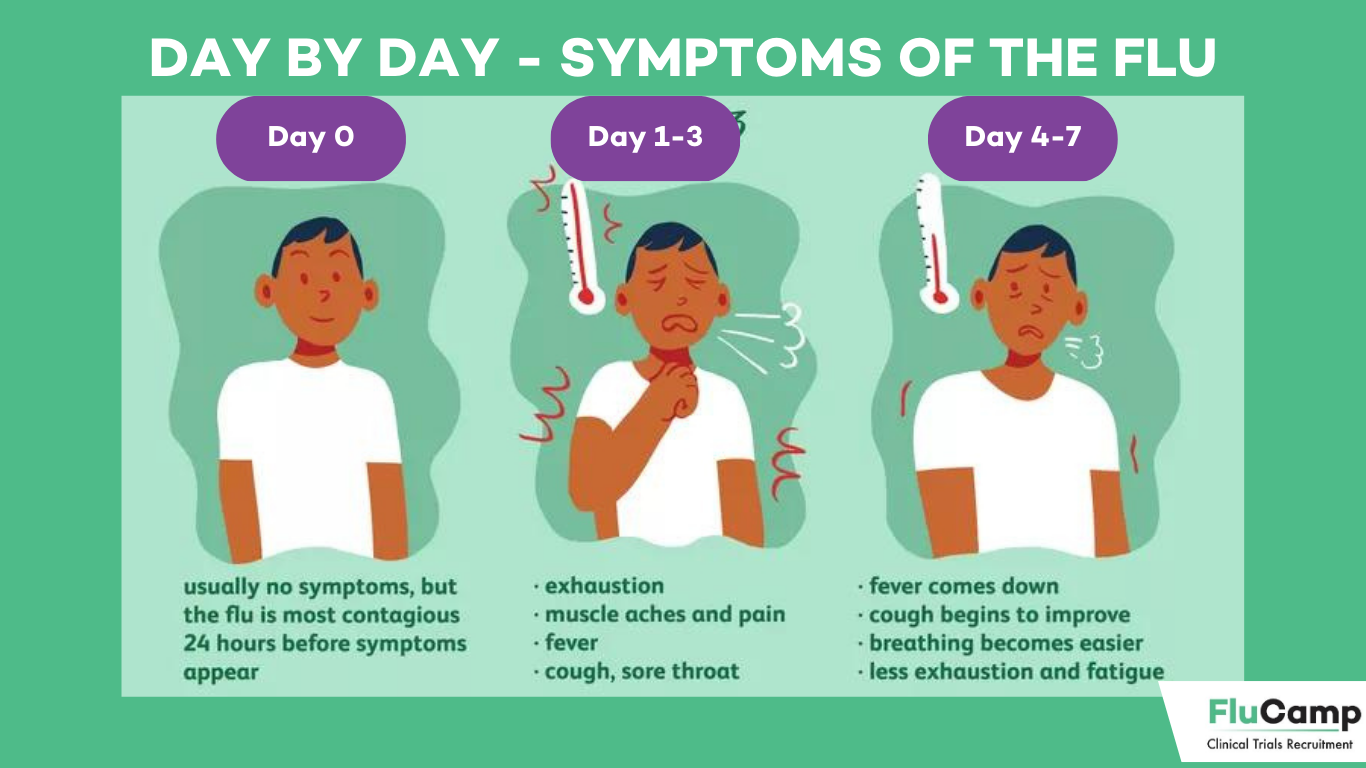
How Long Does the Flu Last?
One of the most common questions people have is, “How long does the flu last?” The duration of the flu can vary from person to person, but typically, the flu lasts about 5 to 7 days. However, some symptoms, like fatigue and cough, can persist for two weeks or more.
Stages of the Flu
1. Incubation Period
The incubation period for the flu is usually 1 to 4 days, with an average of about 2 days. During this time, the virus is multiplying in the body, and the infected person may not yet show symptoms but can still spread the virus to others.
2. Symptomatic Phase
The symptomatic phase is when the flu symptoms become apparent. This phase typically lasts 3 to 7 days. During this time, individuals are most contagious, especially in the first 3 to 4 days after their illness begins.
3. Recovery Phase
After the acute symptoms subside, recovery begins. Some symptoms, such as fatigue and cough, may linger for a week or more after the initial illness. It’s essential to continue resting and hydrating during this phase to aid recovery.
Factors Influencing Flu Duration
Several factors can influence how long the flu lasts, including:
- Age: Children and older adults may experience longer and more severe symptoms.
- Health Status: Individuals with weakened immune systems or chronic health conditions may have prolonged illness.
- Vaccination Status: Those who receive the flu vaccine may experience milder symptoms and shorter illness duration.
- Viral Strain: Different strains of the influenza virus can cause varying severity and duration of illness.
Managing Flu Symptoms
While there is no cure for the flu, several strategies can help manage symptoms and shorten the duration of illness:
Rest and Hydration
Getting plenty of rest and staying hydrated are crucial for recovery. Drinking fluids like water, herbal teas, and broths can help prevent dehydration.
Over-the-Counter Medications
Over-the-counter medications, such as acetaminophen or ibuprofen, can help reduce fever and alleviate body aches and pains. Always follow the instructions on the label and consult with a healthcare professional if needed.
Antiviral Medications
In some cases, healthcare providers may prescribe antiviral medications, such as oseltamivir (Tamiflu) or zanamivir (Relenza), to reduce the severity and duration of the flu. These medications are most effective when taken within the first 48 hours of symptom onset.
Preventing the Flu
Prevention is the best strategy against the flu. Here are some effective ways to reduce the risk of contracting the flu:
Get Vaccinated
The flu vaccine is the most effective way to prevent the flu. It is recommended for everyone aged six months and older, with rare exceptions. The vaccine is updated annually to protect against the most common strains of the virus.
Practice Good Hygiene
- Wash your hands frequently with soap and water for at least 20 seconds.
- Use hand sanitizer when soap and water are not available.
- Avoid touching your face, especially your eyes, nose, and mouth.
- Cover your mouth and nose with a tissue or your elbow when you cough or sneeze.
Avoid Close Contact
Try to avoid close contact with sick individuals. If you are sick, stay home from work, school, and public places to prevent spreading the virus to others.
When to Seek Medical Attention
While most people recover from the flu without needing medical treatment, it’s important to seek medical attention if you experience severe symptoms or complications, such as:
- Difficulty breathing or shortness of breath
- Chest pain or pressure
- Sudden dizziness or confusion
- Severe or persistent vomiting
- Symptoms that improve but then return with fever and worse cough
Understanding how long the flu lasts and how to manage symptoms can help individuals navigate flu season with greater ease. While the flu typically lasts about a week, taking preventive measures and managing symptoms effectively can lead to a quicker recovery. Remember, the flu vaccine is the best defense against the virus, and practicing good hygiene can help protect you and those around you.